 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Basics
- GLBA Safeguards Rule compliance in higher education checklist
- IsoraGRC for GLBA Safeguards Rule
Welcome to the 2024 edition of our Complete Guide, GLBA Compliance in Higher Education. This Complete Guide is an essential extension of our broader guide for higher education institutions, Understanding the GLBA Safeguards Rule, Complete Guide.
Introduction
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) has been a requirement for financial institutions since it came into effect in 1999, but it has directly impacted Title IV colleges and universities since 2018. In particular, the GLBA Safeguards Rule is included in the Federal Single Audit and the Student Aid Internet Gateway (SAIG) agreement and is regulated by The Department of Education and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
All higher education institutions that handle financial student aid data must implement information security safeguards as prescribed in the Final Rule (CFR 314), which took effect on June 9, 2023.
This comprehensive guide from SaltyCloud equips you with essential insights into the GLBA, its Safeguards Rule, and the specific regulatory requirements affecting higher education institutions to help you successfully navigate and ace your regulatory audits.
Understanding the Basics
What is the GLBA?
The GLBA is federal legislation that mandates financial institutions to be transparent about their information-sharing practices and to take robust measures to secure sensitive consumer data.
What is the GLBA Safeguards Rule?
The GLBA Safeguards Rule is a regulatory framework that mandates financial institutions implement comprehensive security measures to protect customer data through an Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) program. Initially established in 2003 and known formally as the Standards for Safeguarding Customer Information, the rule outlines a multi-layered approach involving administrative, technical, and physical safeguards. Its primary goal is to ensure the security and privacy of customer information. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) most recently updated these guidelines on December 9, 2021, with the amendments, termed the Final Rule, becoming effective on June 9, 2023.
The GLBA Safeguards Rule is a regulatory framework that mandates financial institutions implement comprehensive security measures to protect customer data.
Does GLBA apply to higher education institutions?
Yes, as of June 9, 2023, the GLBA Safeguards Rule applies to all Title IV colleges and universities and is included in the SAIG agreement and the Federal Single Audit.
History
Over the last ten years, the Department of Education’s Student Financial Aid Office (FSA) has been ramping up its scrutiny of how educational institutions meet their legal requirements for safeguarding student financial data. This increased focus has been communicated through various critical notices and guidance documents:
Over the last ten years, the Department of Education’s Student Financial Aid Office (FSA) has been ramping up its scrutiny of how educational institutions meet their legal requirements for safeguarding student financial data.
- July 2015: A Dear Colleague Letter (GEN-15-18) stressed institutions’ responsibilities under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) to secure student financial data, advocating for adherence to industry standards and security best practices.
- February 2016: Another Dear Colleague Letter (GEN-16-12) informed schools that annual audits would commence to enforce GLBA compliance. This notice emphasized schools’ commitment, through their Program Participation Agreement, to meet GLBA standards. It also “strongly encouraged” institutions to understand and address gaps in NIST 800-171 controls.
- January 2019: A detailed letter from the Office of Inspector General (CPA-19-01) outlined the audit procedures assessing institutions’ adherence to GLBA safeguards.
- February 2020: An Electronic Announcement specified the penalties for failing GLBA compliance audits, including potential FTC referrals or losing access to Department systems.
- December 2020: Another Electronic Announcement advocated adopting the NIST 800-171 information security framework to support continuous GLBA compliance. Though the FSA introduced a “Campus Cybersecurity Program,” there hasn’t been noticeable progress on this front.
- February 2023: A General Announcement (GENERAL-23-09) encapsulated the Federal Trade Commission’s recent amendments to GLBA, which include nine essential safeguard elements.
- May 2023: A subsequent General Announcement (GENERAL-23-34) disclosed upcoming obligations to treat Federal Tax Information (FTI) as Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), starting from the 2024-2025 FAFSA cycle, while reiterating the importance of adhering to NIST 800-171.
- September 2023: An Electronic Announcement (GENERAL-23-79) announced that partners must sign an updated SAIG enrollment agreement by October 23, 2023, to receive 2024-25 and future ISIRs containing FTI.
Regulatory oversight
The Department of Education and FSA employ two main tools to enforce compliance with the GLBA: the Student Aid Internet Gateway (SAIG) Agreement and the Federal Single Audit. While they differ slightly, they require institutions to maintain an information security program, conduct periodic risk assessments, and address findings.
The Department of Education and FSA employs two main tools to enforce compliance with the GLBA
Student Aid Internet Gateway (SAIG) Agreement
The SAIG Agreement enables the electronic transfer of financial aid data between educational institutions and the Department. A key update in September 2022 mandated that institutions affirm full compliance with the enhanced GLBA Safeguards Rule. This rule requires compliance with 16 CFR 314.3 and 314.4 in its entirety.
The Department announced that partners must sign an updated SAIG enrollment agreement by October 23, 2023, to receive 2024-25 and future Institutional Student Information Records (ISIRs). This updated agreement acknowledges the penalties for unauthorized inspection or disclosure of FTI and will enable ISIRs containing FTI to be received in a new FTI-SAIG mailbox.
While specific details are still pending on potential NIST 800-171 compliance requirements, the revised agreement will likely mandate compliance that aligns with the July 1, 2024, deadline for new FTI handling procedures under the FAFSA Simplification Act. Institutions should take the necessary steps to sign the updated agreement and prepare for the FTI-SAIG mailbox to continue receiving ISIRs.
Federal Single Audit
An annual procedure, the Federal Single Audit reviews how well institutions receiving federal funds follow regulations. Starting in the fiscal year 2019, it added GLBA compliance goals and its scope was widened in the fiscal year 2023 to reflect the updated Safeguards Rule. Contrary to the SAIG agreement, the Federal Single Audit focuses on verifying only seven out of the nine required safeguards from 16 CFR 314.4(c).
GLBA vs. FERPA vs. HEA
When it comes to safeguarding student data, higher education institutions must often navigate a triad of critical regulatory frameworks: the GLBA, the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), and the Higher Education Act (HEA). Although these regulations may have points of intersection—for instance, financial aid data can simultaneously fall under educational records—they each have unique objectives, scopes, and compliance criteria.
GLBA Safeguards Rule: Centered on financial records
GLBA concentrates on fortifying the security of financial information. It obliges financial institutions and educational entities that handle FSA data to establish a formal, structured information security program. This program has a far-reaching scope, covering elements like student loans, tuition payments, and other fiscal records.
FERPA: Centered on educational records
FERPA is tailored to protect educational records, such as grades, transcripts, and student attendance. The law clearly defines who can access these records, requiring explicit consent from the student or their guardians if the student is underage. FERPA does not offer a prescriptive security framework like GLBA but demands tight control and restricted disclosure of educational records.
HEA: A broad umbrella
HEA serves as an overarching legislative framework for federal student aid programs. While its primary focus isn’t data privacy per se, HEA does impose specific requirements related to the disclosure of information and data retention. Under HEA, institutions must maintain records for federal student aid programs and ensure that this data aligns with GLBA and FERPA guidelines where applicable.
Evolving information security regulations in higher education
The regulatory environment for higher education is intensifying, with newer compliance demands such as the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) for institutions engaged with the Department of Defense. Simultaneously, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) has broadened its scope, now implicating the ways in which educational institutions process and safeguard financial information. Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) programs are at the heart of these regulatory dynamics. They establish the infrastructure through which institutions assess risks, enforce data protection controls, and ensure compliance across their information systems. By anchoring their security strategies in ISRM, universities can adeptly manage the spectrum of risks while maintaining compliance with existing and emerging regulations.
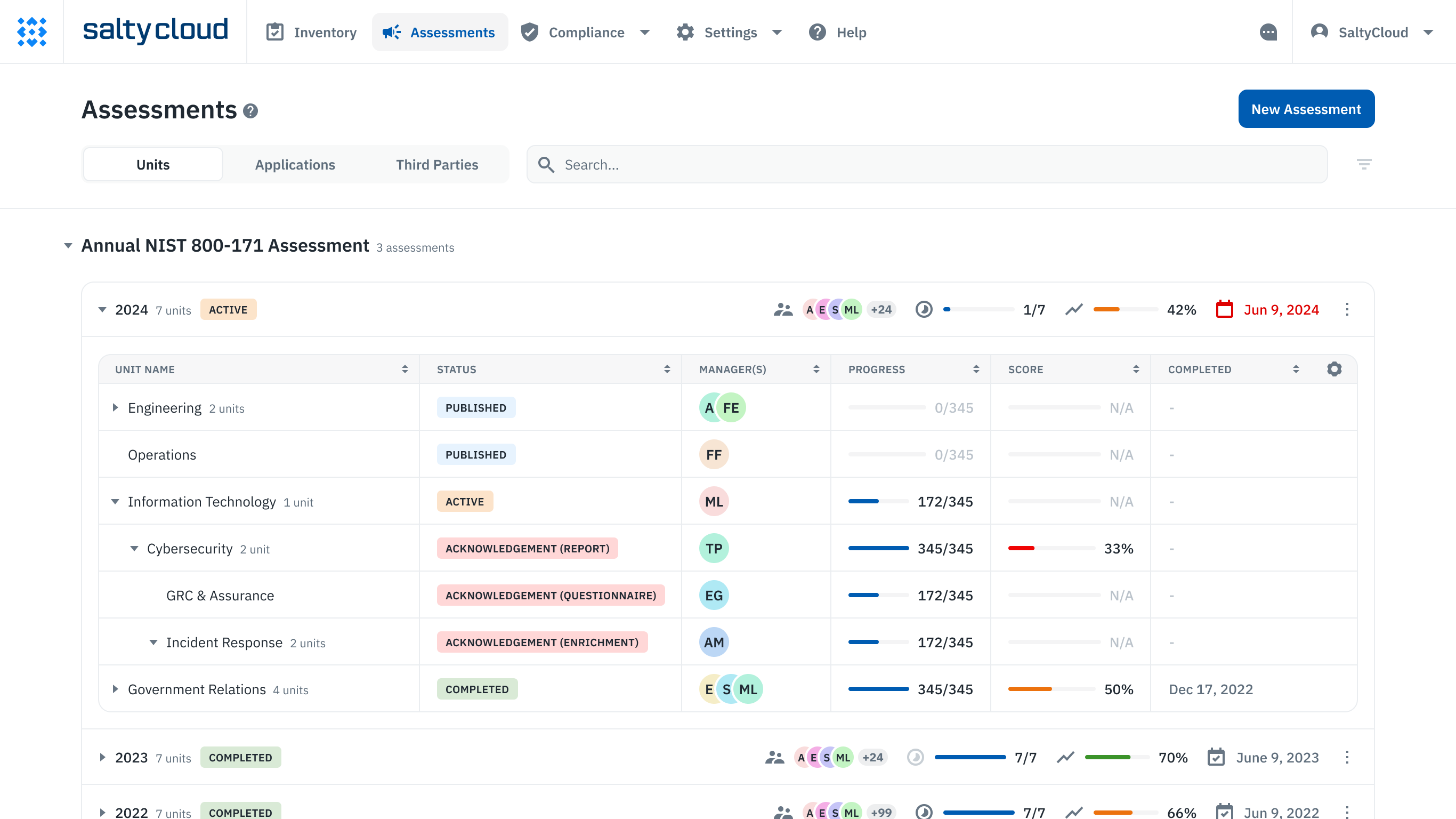
Assessment management dashboard in Isora GRC.
By anchoring their security strategies in ISRM, universities can adeptly manage the spectrum of risks while maintaining compliance with existing and emerging regulations.
Isora is a collaborative GRC platform that empowers everyone to own risk together with user-friendly and flexible tools. With Isora, teams can stay agile and responsive to growing changes, fostering a resilient organizational culture. With user-friendly tools for conducting risk assessments, teams of all sizes can navigate the complexities of evolving regulations while working toward cyber resilience.
Is student data considered CUI in higher education?
Yes, but the scope is nuanced. Federal Tax Information (FTI) used in financial aid processes has been specifically designated as Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) by the Department of Education, effective from the 2024-2025 FAFSA cycle (GENERAL-23-34). In addition, the department has indicated that most data related to student aid is considered CUI and has issued statements urging institutions to align with NIST 800-171 controls (GEN-16-12). In a follow-up 2020 communication (Electronic Announcement), the department informed institutions of its intention for them to comply with NIST 800-171 and added that “most data sourced from the Department and information used in the administration of Title IV programs are considered CUI.”
Educational institutions act as federal contractors when administering Student Financial Aid (SFA) programs.
Educational institutions act as federal contractors when administering Student Financial Aid (SFA) programs. This role obligates them to protect both the CUI they receive from the Federal Government and any CUI they generate in the administration of their SFA program. According to the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA), student records are already an existing category of CUI, so it’s likely only a matter of time before the department officially designates SFA data as CUI in contracts.
Federal security protocols, outlined in the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) and NIST 800-53, extend to data shared with contractors. These protocols require contractors to include NIST 800-171 compliance in contracts where CUI leaves the federal government. This is supported by the Department of Education’s GEN-16-12 and December 2020 letters, which specifically cite NIST 800-171 as the recommended requirements for safeguarding certain federal information.
As the Department of Education prepares to receive and disseminate more CUI, specifically FTI, from the IRS, it’s reasonable to expect that NIST 800-171 requirements will be extended to cover this additional data sharing. Given federal guidelines and the IRS’s own data sensitivity, stringent security measures aligned with NIST 800-171 are likely to be in place for the transfer of FTI.
What are the penalties for GLBA noncompliance in higher education?
Noncompliance with the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) in higher education can lead to a cascade of immediate and long-lasting penalties. Initial actions often involve sharing audit findings related to safeguard deficiencies with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), the regulator for GLBA, and the Federal Student Aid’s Postsecondary Institution Cybersecurity Team. Both entities could take further actions based on these findings.
Noncompliance with the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) in higher education can lead to a cascade of immediate and long-lasting penalties.
Legal penalties are delineated under Section 523 of the GLBA, which allows institutions to incur fines of up to $100,000 and individuals responsible for violations to face imprisonment for up to five years, extendable to ten years for repeat offenses.
However, the most severe and final action that could be taken is disabling an institution’s access to the Department of Education’s information systems. This step, as highlighted in the February 2020 Electronic Announcement, would effectively nullify an institution’s ability to administer Student Financial Aid (SFA), severely impacting its capacity to enroll most students.
The risk of a security breach also looms large, potentially leading to unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive student information. Such an event could compel the institution to pay substantial ransoms for data retrieval without assurance of data return. Beyond the immediate financial toll, these security lapses can damage an institution’s reputation, causing students and the general public to question its credibility.
GLBA Safeguards Rule compliance in higher education checklist
Understand the GLBA Safeguards Rule
Begin by comprehending the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act’s Safeguards Rule (16 CFR Part 314). You’ll be tasked with establishing an information security program, designating a program manager, and implementing an IT & security risk management program that focuses on identifying, tracking, and mitigating security risks.
Do your homework. Figure out what the GLBA Safeguards Rule entails (CFR 314). You’ll need to maintain an information security program, assign an individual to oversee said information security program, and implement an Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) program, which will involve identifying, tracking, and remediating risks.
Scope your institution
Not all parts of your institution are subject to the GLBA Safeguards Rule. As the regulatory landscape evolves, it’s essential to maintain a comprehensive IT asset and third-party inventory that includes data storage locations, data classification, and responsible parties. While only Federal Tax Information (FTI) is currently designated as Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), it’s prudent to prepare for potential future expansions of this classification by the Department of Education to include all data used in the administration of student financial aid programs.
To adopt a robust asset categorization and inventory approach, consider the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) framework, specifically targeting CMMC Assessment Scope – Level 2, which is based on NIST 800-171. Begin by meticulously cataloging all assets: servers, endpoints, mobile devices, network equipment, IoT systems, data centers, and cloud services. Add details such as hardware specifications, software versions, ownership, and physical locations.
Next, align these assets with CMMC asset categories, focusing on their interaction with CUI and all data processed, stored, or transmitted as part of your Student Financial Aid (SFA) program, including FTI from the IRS. For a more nuanced categorization, consider the following:
- Process: Assets that engage with CUI or FSA data in any capacity—whether accessed, entered, edited, generated, manipulated, or printed—fall under this category.
- Store: This category includes assets where CUI or FSA data is inactive or at rest, such as data located on electronic media, in system component memory, or in physical formats like paper documents.
- Transmit: Assets involved in transferring CUI or FSA data from one location to another, whether physically or digitally, belong to this category.
Collaborate and prepare
Success in complying with the GLBA Safeguards Rule hinges on implementing a nuanced, risk-based information security program. It’s a continual effort that requires committed collaboration from various institutional stakeholders, from IT professionals to institutional leadership.
Key players in this collaborative initiative should include:
- The designated manager overseeing the information security program (potentially you)
- IT staff responsible for the assets subject to the GLBA Safeguards Rule
- Business units that process, store, or transmit the covered data
- Leadership figures, both within specific business units and at the institutional level
It’s worth noting that according to the Student Aid Internet Gateway (SAIG) agreement, the institution’s president or CEO must sign an attestation confirming compliance with the GLBA Safeguards Rule’s nine elements, as outlined in 16 CFR Part 314.
Flexibility is critical when it comes to selecting a security framework. Although neither the GLBA Safeguards Rule nor the Department of Education specifies a required framework, NIST 800-171 is often recommended. Alternatives like NIST’s Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF), NIST 800-53, the Center for Internet Security’s Critical Security Controls (CIS), or ISO/IEC 27001 are also viable options. However, it’s important to be forward-looking: the federal government mandates NIST 800-171 for handling Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Given this, there’s a strong likelihood that institutions will need to align with NIST 800-171 in the near future, potentially even before the next academic year kicks off and they start receiving Federal Tax Information (FTI).
Conduct your risk assessment
Conducting a thorough risk assessment is a pivotal step toward compliance with the GLBA Safeguards Rule. This process involves a detailed analysis across all relevant business units, including any third-party vendors that might impact your data security posture. Choosing an information security risk management framework, such as NIST 800-39 or ISO/IEC 27005, can serve as a solid foundation for this assessment. The goal of your GLBA Safeguards Rule risk assessment is to pinpoint areas of non-compliance, classify identified risks, and strategize on prioritizing their mitigation.
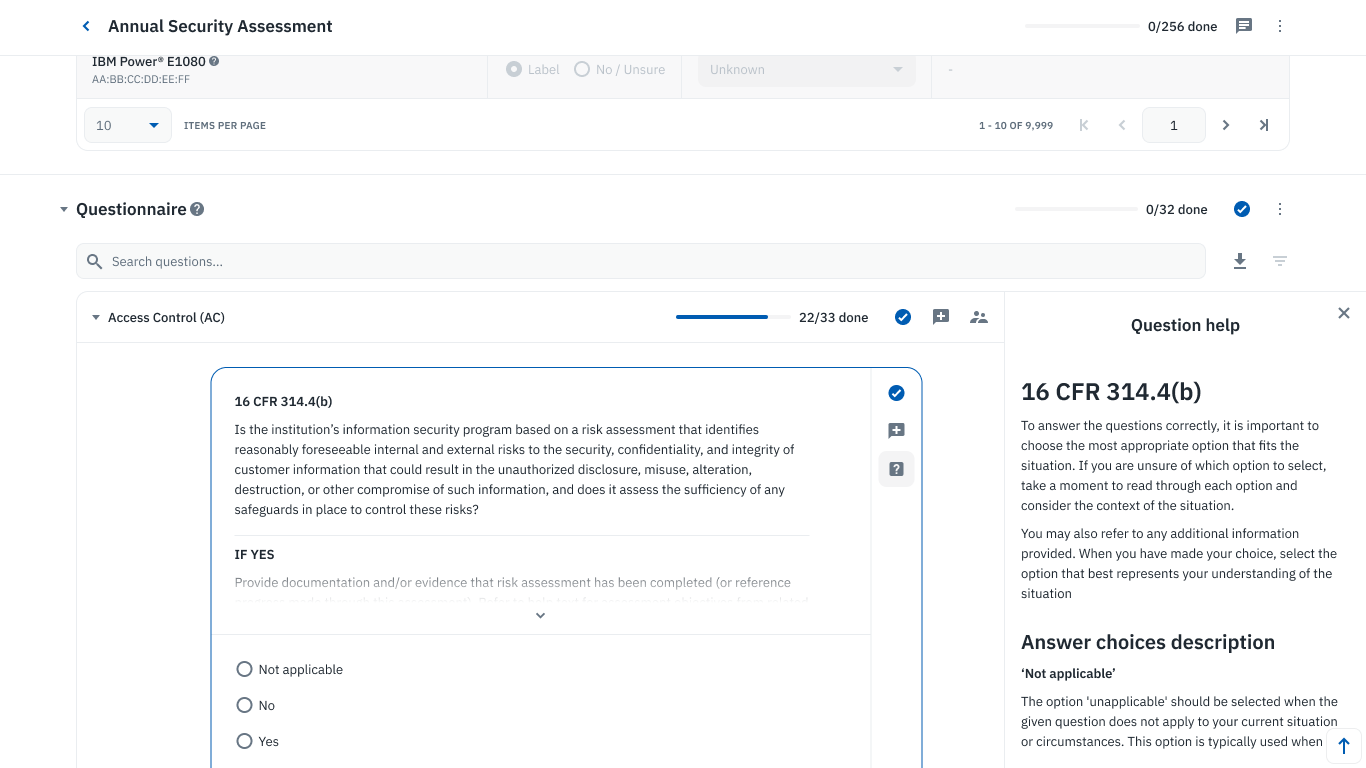
Collaborative questionnaire on Isora GRC.
The goal of your GLBA Safeguards Rule risk assessment is to pinpoint areas of non-compliance, classify identified risks, and strategize on prioritizing their mitigation.
Isora is the #1 GRC platform for higher education information security teams, providing the necessary tooling and templates to conduct risk assessments, collect evidence, and track risks so you can ace your GLBA Safeguards Rule audit and build cyber resilience.
Track, prioritize, remediate, and reassess
After your initial risk assessment, you’ll likely have a set of findings that require attention. Business units must demonstrate full compliance to fulfill the SAIG agreement and Federal Single Audit stipulations. Collaborate with stakeholders to prioritize these findings, assign owners, brainstorm remediation plans, set deadlines, and reassess to track progress. Utilizing a collaborative risk register is highly effective for tracking, assigning, and detailing these risks.
It’s crucial to note that, according to the SAIG agreement, the institution’s president or CEO must sign an attestation stating, “I have ensured that the Standards for Safeguarding Customer Information, as applicable to my institution (See Glossary), 16 C.F.R. Part 314, issued by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), as required by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley (GLB) Act, P.L. 106-102 have been implemented. I understand that failure to implement the requirements of the GLB Act may be considered a lack of administrative capability under 34 C.F.R. § 668.16 by the Secretary.”
Ace your audit
Your compliance will be vetted during an audit, aligning with SAIG attestations and Federal Single Audit requirements. To facilitate this, compile all your assessment data, documentation, and evidence in a user-friendly manner. If you’re using a platform like Isora, you can give auditors access to your historical assessments, asset inventories, supporting evidence, and risk register to streamline the audit process.
Isora GRC for GLBA Safeguards Rule
The GLBA Safeguards Rule isn’t just a regulatory guideline; it’s a mandate with severe implications for non-compliance. At its core, the rule calls for organizations to establish a robust Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) program, maintain an IT asset inventory, continuously assess risks across covered business units and third parties, and provide board-level reporting.
Isora is a collaborative GRC platform that empowers everyone to own risk together with user-friendly and flexible tools. It helps higher education institutions meet the requirements outlined in 16 CFR 314.3 and 314.4 for GLBA Safeguards Rule compliance.
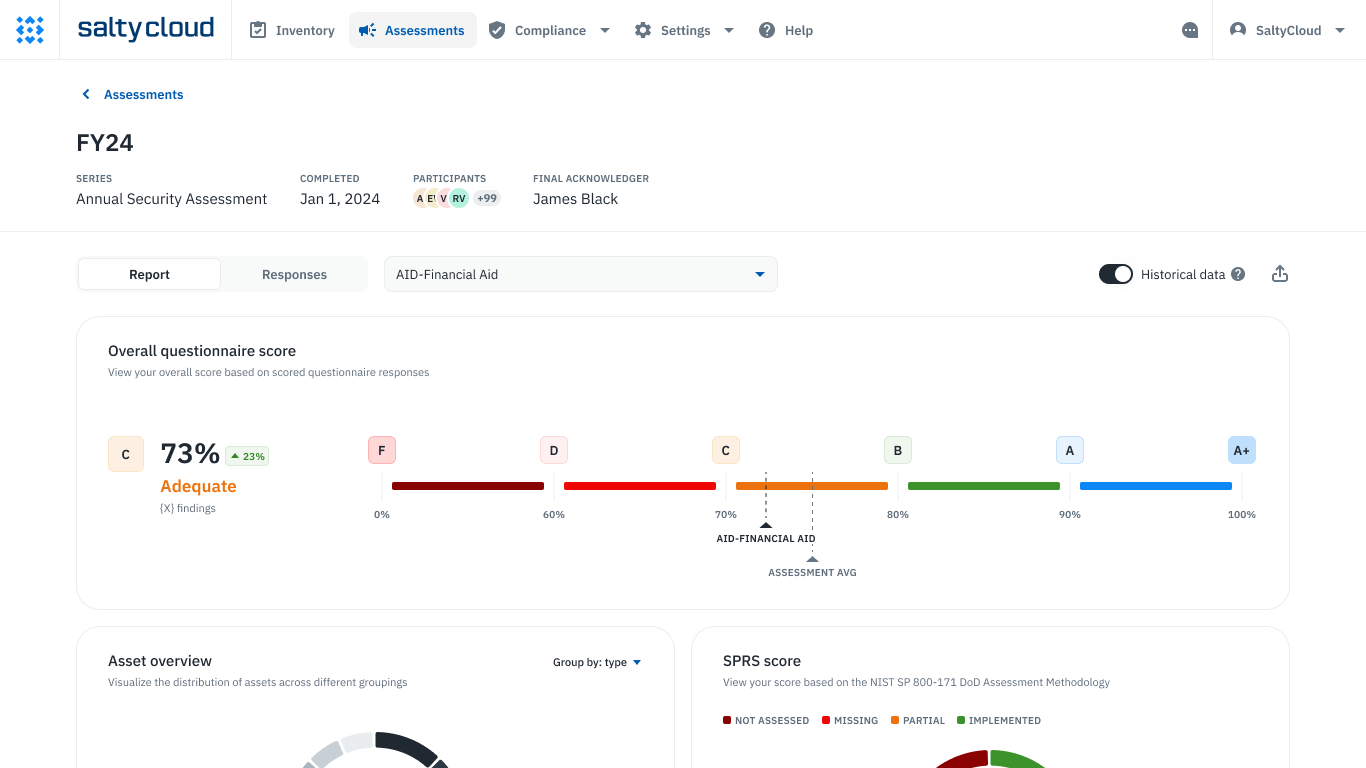
Assessment scorecards and reports in Isora GRC.
With Isora, information security & assurance teams of all sizes can:
✔ Launch custom or prebuilt security questionnaires for risk assessments, allowing internal teams and third parties to answer questions, upload evidence, collaborate, and sign attestations.
✔ Create a centralized inventory of IT assets, applications, and third parties, complete with metadata details like data classification, ownership, and user tracking.
✔ Connect with any other platforms, including existing procurement, risk intelligence, and GRC platforms, to enable the flow of information.
✔ Generate detailed scorecards and risk reports based on completed assessments that help everyone know what needs attention.
Join dozens of established organizations who trust Isora to help them build and scale their GRC programs.
Get a demo to learn how Isora can help your team ace their GLBA Safeguards Rule audit.



















 Other Relevant Content
Other Relevant Content