-
Product Capabilities
-
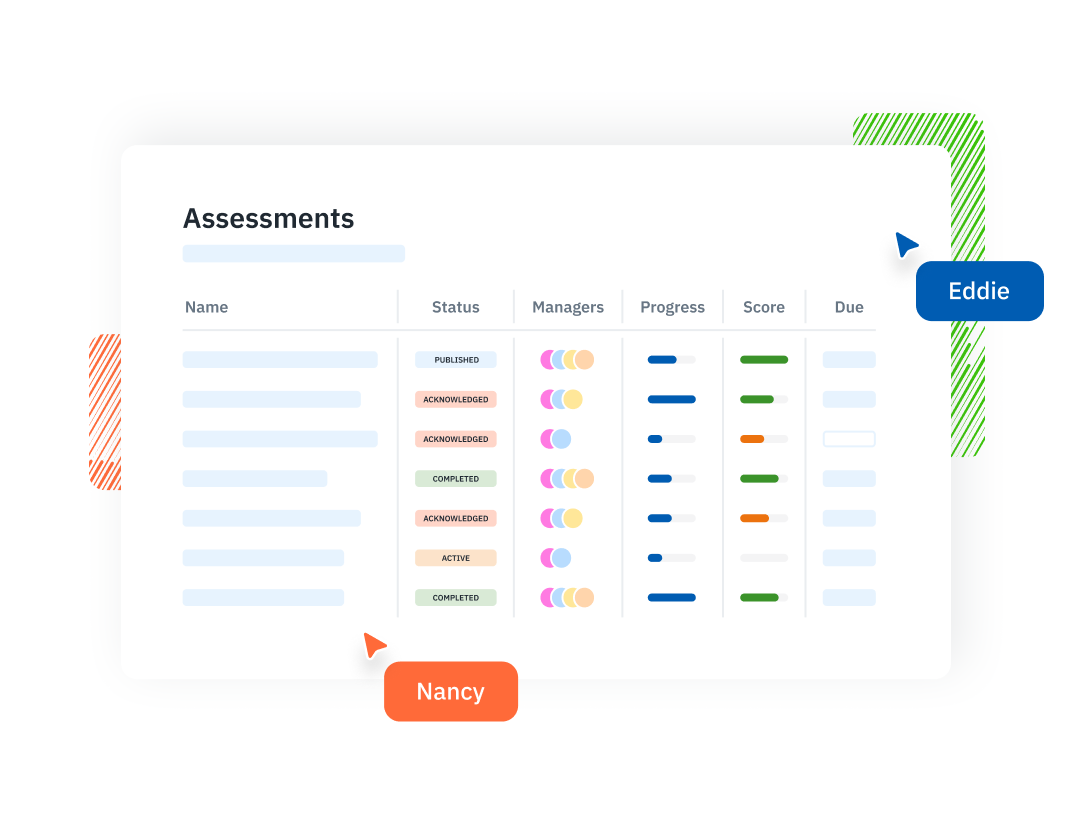
Assessment Management Run structured security assessments across systems, teams, and vendors—all from one place.
-
Questionnaires & Surveys Collect the evidence you need with targeted questionnaires tailored to compliance and risk workflows.
-
Reports & Scorecards Turn assessments into audit-ready reports and actionable insights your team can actually use.
-
Inventory Management Maintain real-time inventories of IT assets, systems, and third parties to support risk and compliance.
-
Exception Management Log, track, and resolve policy exceptions so nothing falls through the cracks during audits.
-
Risk Management Identify, document, and mitigate security risks with workflows that bring clarity and accountability.
Use Cases-
Information Security Risk Management (ISRM) Run assessments across units and systems, maintain IT asset inventories, and collaborate on a shared risk register—all in one place.
-
Third-Party Security Risk Management (TPSRM) Track vendors, send security questionnaires, and manage third-party risk with built-in workflows and a centralized inventory.
This guide contains everything you need to know about conducting an information security risk assessment questionnaire at your organization.
-
-
Solutions FrameworksIndustries
-
Insights Latest ContentLatest Content
- Customer Stories